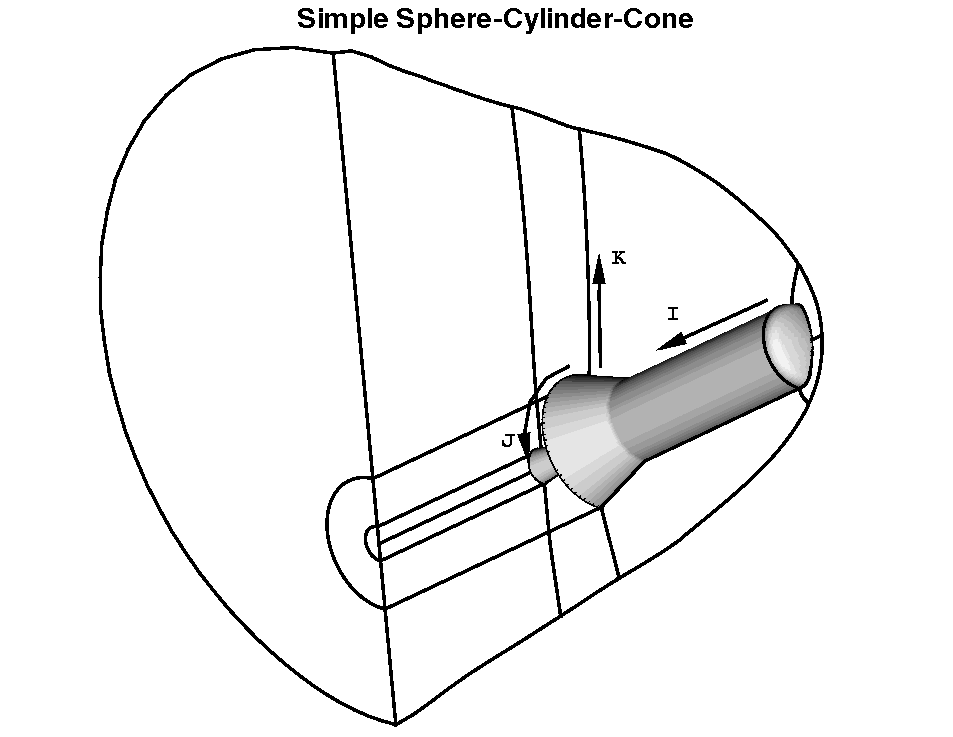
Original Grid and Geometry:
Below is the volume grid that was obtained by using the 3DMAGGS code for volumetric discretization and
the Langley Aerothermodynamic Upwid Relaxation Algorithm (LAURA)
code. The problem posed was to perform multiple zonal adaption where
each zone is separated by some flow feature that may occur across
multiple grid blocks. Shown in the figure below is the domain of the
flow adapted using the LAURA software. Note that only the entropy
gradient furthest from the wall is captured.
Preparing for Grid Adaption:
Utilizing the Parametric Remapping technique of the VGM
software, the multiple zonal grid adaption can be done. Set up of the
technique requires a coarse adaption of the grid based on a selected
flow variable or a multiple set of flow variables. Since both types
are similar, the multiple set is identified here.
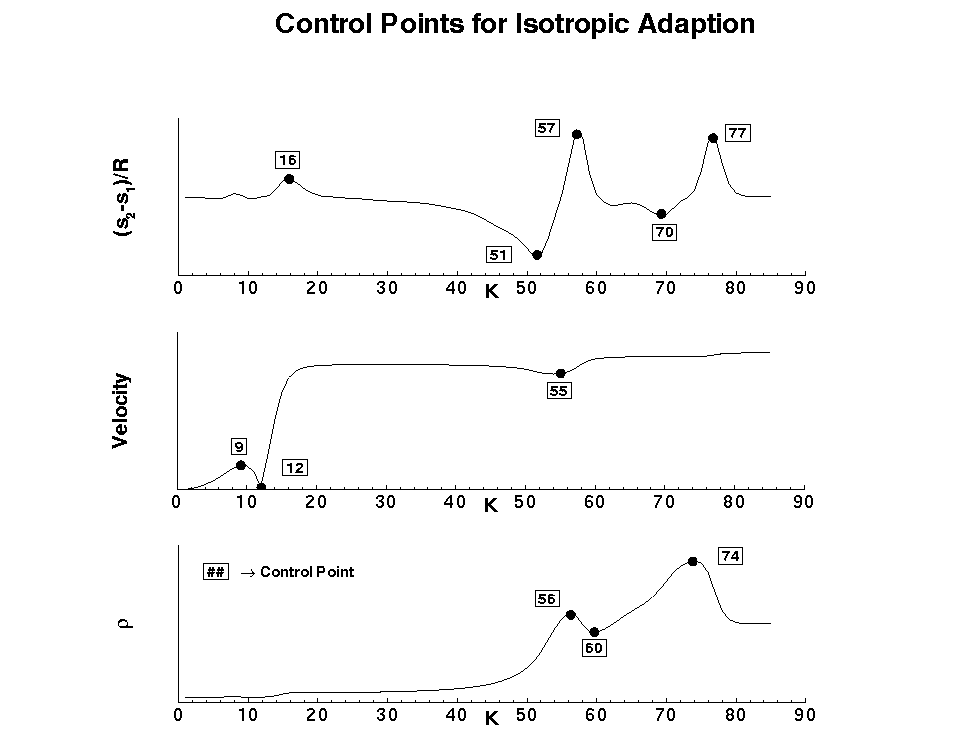
The process of determining how to adapt a grid line begins by
identifying the control points along the line where clustering is to
be created. These control points are usually locations where a flow
variable has an inflection from maximum to minimum and vice
versa. Since the VGM language supports various methods for using the
control points, two are discussed but only the final result is
shown. For the flow field at hand, entropy, density,
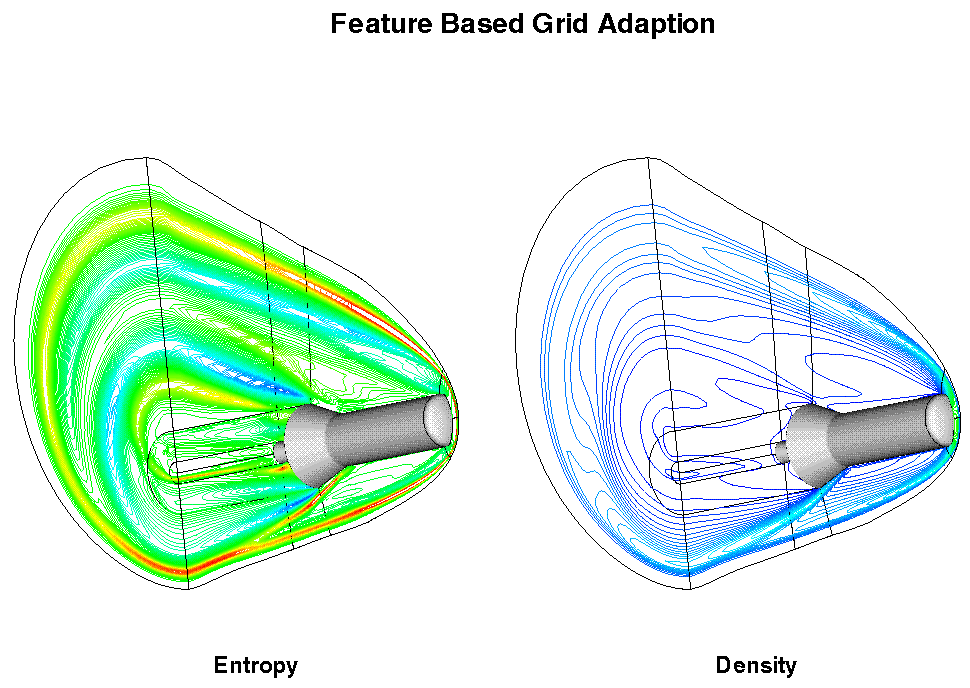
and the magnitude of velocity
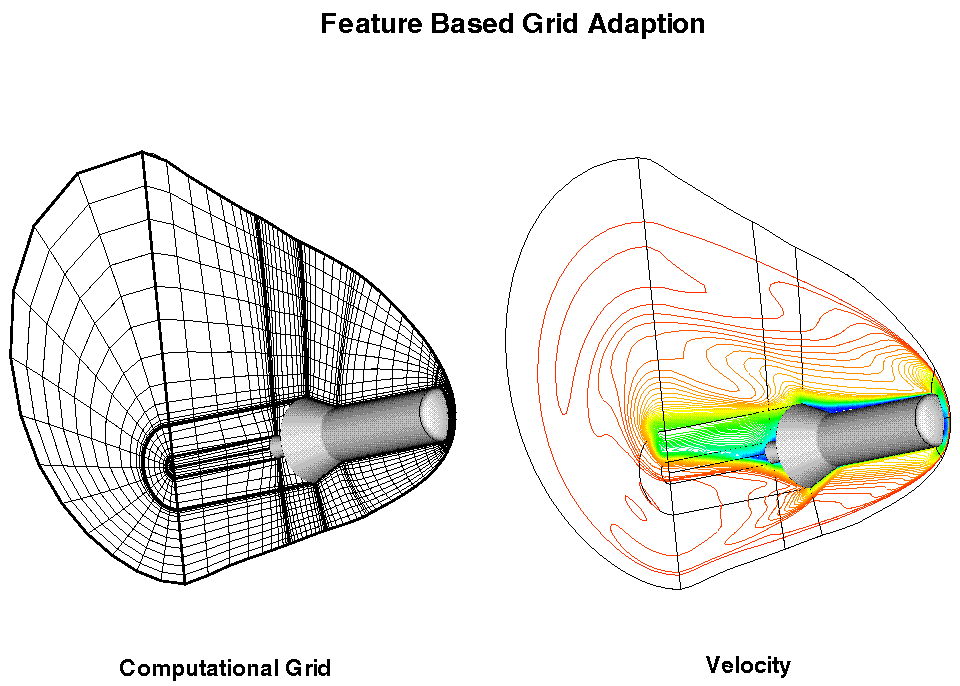
contour profiles are used to identify the control points. Looking
along the K-direction for a single line in the wake of the flow
domain, the control points are easil identified by the plot of the
variables.
Use of these control points can be used to redistribute the available
grid points along the line, one adaption for each flow variable or one
adaption for all three variables. If one adation for each flow
variable is used, the distribution function for the grid line can be
combined by taking one third of each normalized adapted grid line and
summing them to form one distribution function. In either case, a grid
line is adapted to capture the flow variable gradients.
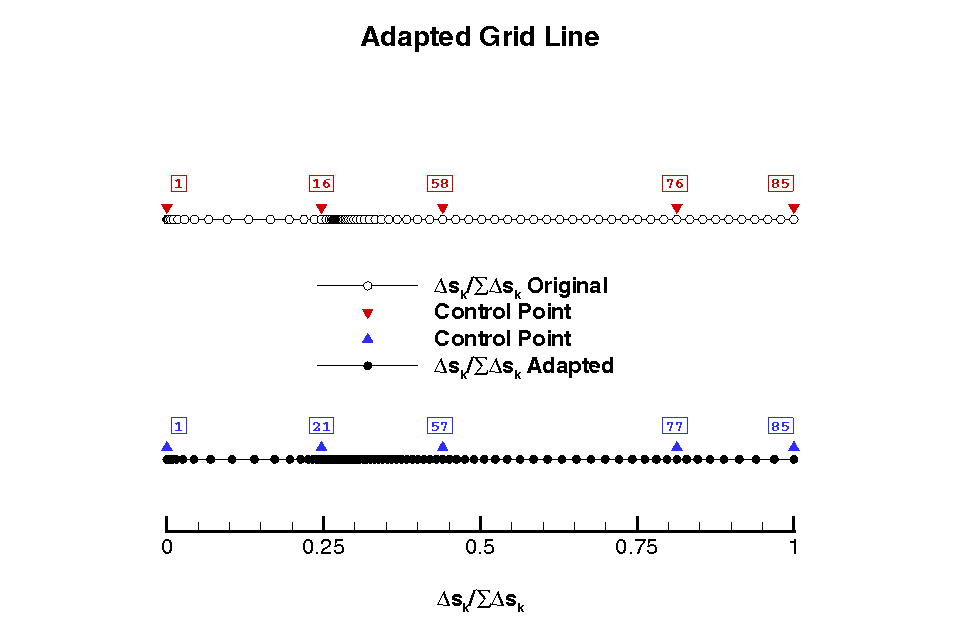
This adaption is performed on a significantly reduced subset of the
volume grid, to obtain a coarse adapted grid.
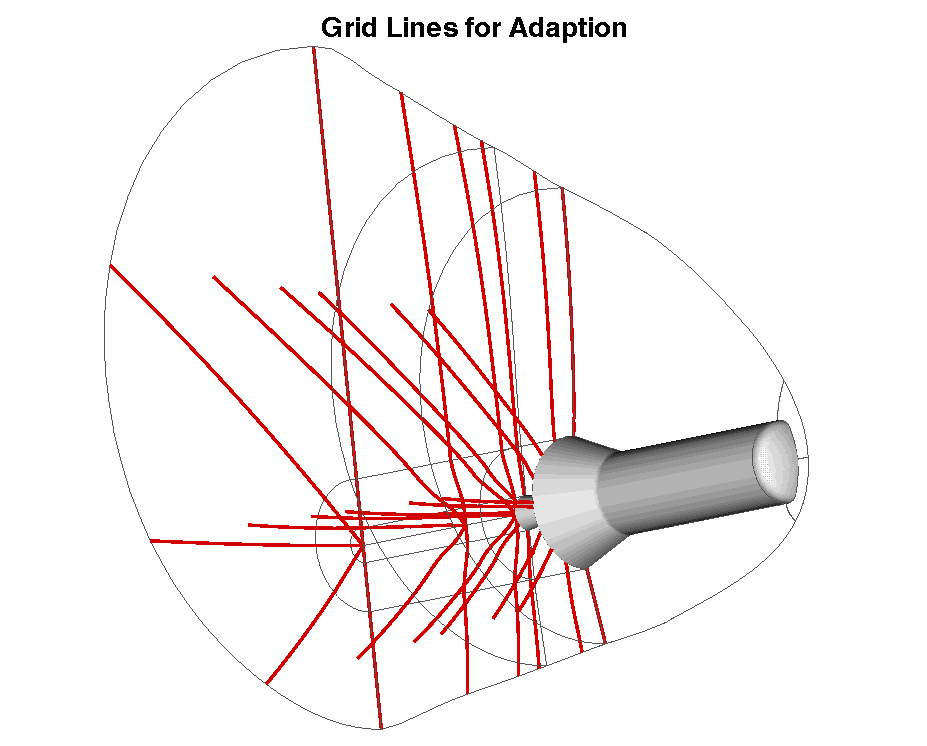
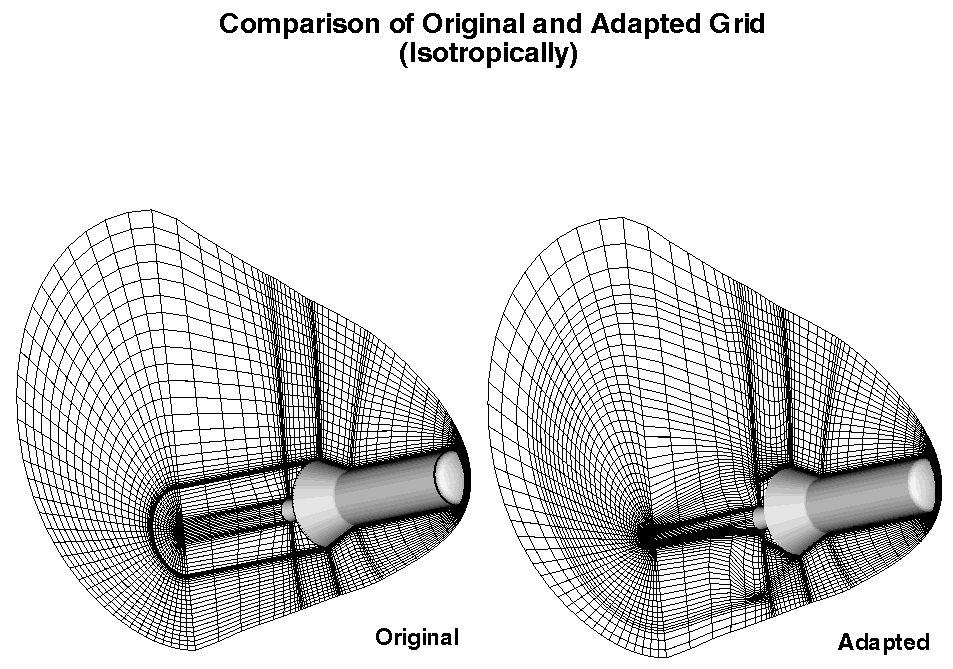
Using the coarse grid as a basis for the remaining adpation of the
volume grid, Parametric Remapping is used to recompute the
distribution function between the adapted grid lines for the
non-adapted grid lines. The new volumetric distribution functions in
the K-direction are then used to perform the final grid adaption which
is shown below, or a complete
(
full grid point density).
NASA Official Responsible for Content --
Stephen J. Alter
Last Updated November 6, 2002
Feedback on Langley Products and Services
